Introduction
In today’s fast-paced ecommerce landscape, effective inventory management plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations and sustainable growth. One of the most powerful tools that helps businesses stay organized and avoid costly stock issues is the Stock Keeping Unit (SKU).
But what exactly is an SKU, and why is it such a game-changer for online and retail businesses? In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know — from SKU meaning and practical examples to how SKUs work, why they matter, and how to build a smart, scalable SKU system that supports your fulfillment strategy.
If you’re looking to optimize your inventory flow, you may also like.
What Is an SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)?
An SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to each individual product or variation in your inventory. It acts like a digital ID, helping businesses track, organize, and manage stock efficiently. This unique identifier allows sellers to differentiate products even when they look or feel similar.
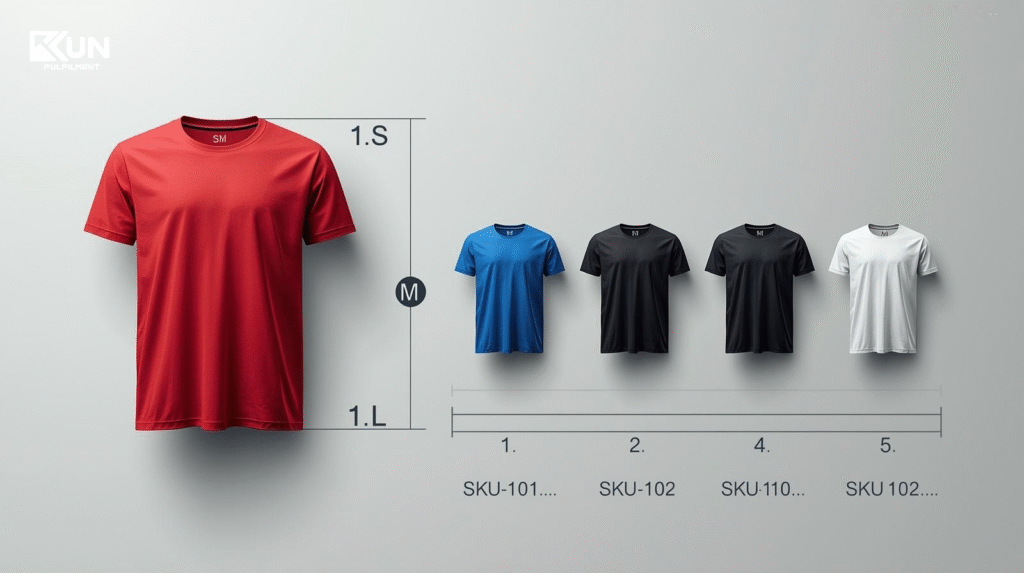
For example, imagine you’re selling a T-shirt in three sizes (S, M, L) and two colors (Red, Blue). Each product variant will have its own SKU:
- TS-RED-S
- TS-RED-M
- TS-BLU-L
With this system, you can easily monitor stock performance, identify which variants are top sellers, detect out-of-stock items, and plan restocking more accurately.
Explore more ways to optimize product tracking.

What Does SKU Stand For?
SKU stands for Stock Keeping Unit.
It’s not just a random code — it’s a structured system businesses use to:
- Identify each product type and variation
- Track stock levels
- Simplify reordering
- Improve warehouse efficiency
Why Are SKUs Important?
SKUs are the backbone of inventory and order management.
Here’s why they’re crucial for any retail, wholesale, or ecommerce business:
- Better Inventory Tracking
SKUs allow you to monitor product movement, sales trends, and stock levels in real time. - Simplified Reordering Process
When an item runs low, its SKU makes it easy to reorder exactly what’s needed. - Improved Warehouse Management
SKUs help warehouse teams locate, pick, and pack items faster. - Data-Driven Decisions
SKU data helps you identify best-sellers, slow-moving stock, and customer preferences. - Seamless Multi-Channel Selling
Whether you sell on Shopify, Amazon, or your own site, SKUs keep your product data consistent everywhere.
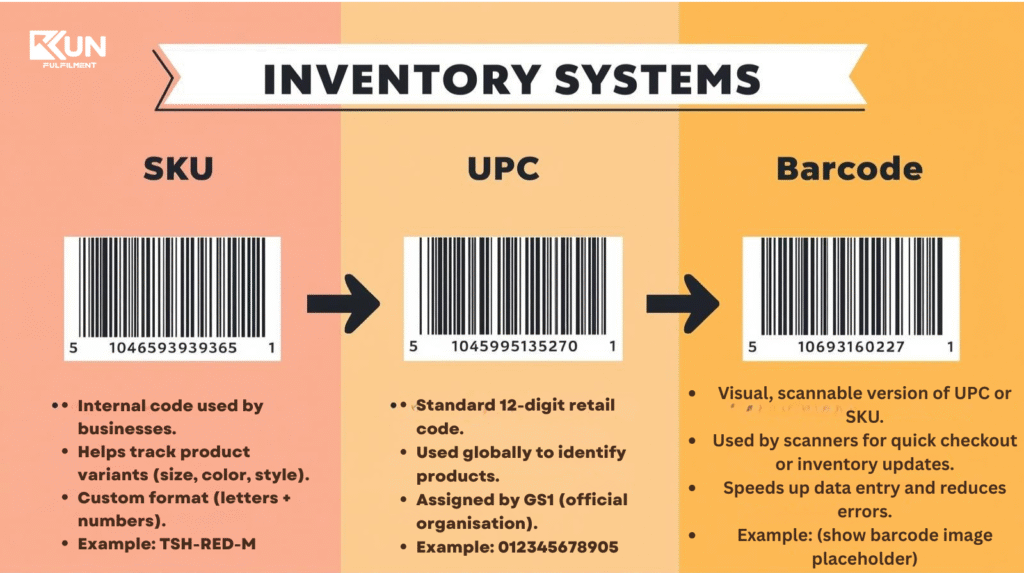
SKU vs. UPC vs. Barcode — What’s the Difference?
Many confuse SKUs with UPC (Universal Product Code) or barcodes, but they are not the same.
| Term | Meaning | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| SKU | Internal product code created by the seller | For inventory and internal tracking |
| UPC | Universal Product Code used globally | For scanning at retail checkout |
| Barcode | Machine-readable version of SKU or UPC | Used for scanning systems |
In short:
SKU = Internal identification
UPC = External identification
How to Create an Effective SKU System
Creating SKUs isn’t about random numbers — it’s a structured process that helps you stay organized.
Here’s a simple format example:
Category – Brand – Attribute – Unique Number
Example: SHO-NIKE-RUN-001
Tips for writing SKUs:
- Keep them short and meaningful (8–12 characters)
- Avoid special symbols (like @ or #)
- Maintain consistency in format
- Reflect product attributes (color, size, style)
- Don’t reuse old SKUs
SKU Example in Retail and Ecommerce
Here’s how a clothing brand might structure its SKUs:
| Product | SKU |
|---|---|
| Men’s White Shirt (Medium) | MSH-WHT-M |
| Women’s Red Dress (Small) | WDR-RED-S |
| Unisex Hoodie (Large, Blue) | UHD-BLU-L |
Each SKU quickly tells you who it’s for, what it is, its color, and size.
Benefits of Using SKUs in Your Business
- Reduces stock errors
- Improves order accuracy
- Saves time during audits
- Helps forecast demand
- Enables automation in ecommerce platforms
With SKUs, you gain better control over your supply chain and reduce costly mistakes.
Learn more about ecommerce businesses.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using random or unstructured codes
- Creating duplicate SKUs
- Changing SKUs frequently
- Not aligning SKUs with product attributes
A consistent system prevents confusion and saves hours of manual correction later.
How SKUs Work in Warehousing and Fulfilment
In modern fulfilment centres, SKUs play a major role in product identification and tracking.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) rely on SKU codes to:
- Locate storage bins
- Track product movement
- Streamline picking, packing, and shipping
This efficiency helps reduce human error and speeds up delivery — crucial for ecommerce success.
How SKUs Support Ecommerce Platforms
Online platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, and eBay require SKUs for product listings.
They:
- Sync inventory across sales channels
- Help avoid overselling
- Provide detailed analytics on performance
If you sell the same product across multiple marketplaces, consistent SKUs ensure all platforms stay in sync.
Conclusion
SKUs may seem like small codes, but they hold the key to a smooth-running inventory system.
By implementing a well-structured SKU system, you’ll save time, reduce mistakes, and gain valuable insights into your business performance.
Whether you’re a small retailer or a growing ecommerce brand, mastering SKUs is a simple step toward smarter inventory management and faster business growth.

